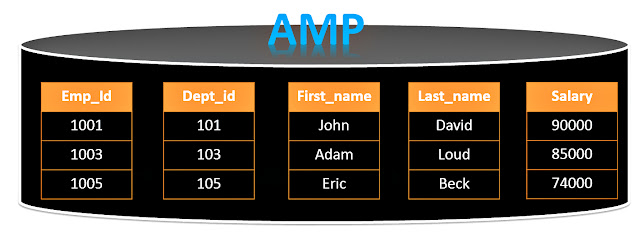
The purpose of a Columnar(NoPI) table is to spread the rows evenly across the AMPs. This is why a NoPI table is often used as a staging table.
Columnar Table Fundamentals
Normal table vs columnar table
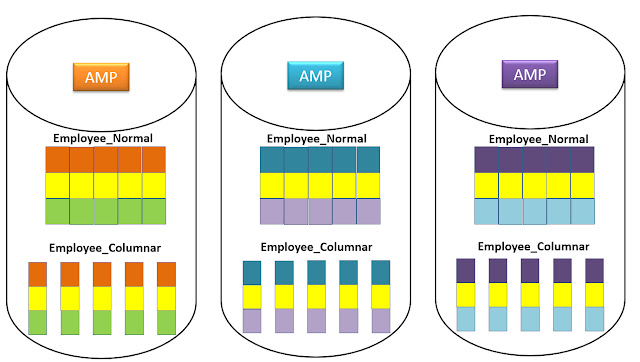
The two tables above contain the same Employee data, but one is a columnar table. Employee_Normal has placed 3 rows on each AMP with 5 columns. The other table Employee_Columnar has 5 Containers each with one column.
Example
CREATE Table Employee
(
Emp_Id Integer
,Dept_Id Integer
,First_Name Varchar(20)
,Last_Name Char(20)
,Salary Decimal (10,2)
)
No Primary Index
PARTITION BY COLUMN;
Columnar table
NoPI Table Capabilities:
NoPI Table Restrictions
Examples of Columnar tables
Multi-Columnar
CREATE Table Employee
(
Emp_Id Integer
,Dept_Id Integer
,First_Name Varchar(20)
,Last_Name Char(20)
,Salary Decimal (10,2)
)
No Primary Index
PARTITION BY COLUMN
(Emp_Id
,Dept_id
(,First_name, Last_name, Salary));
Row Hybrid Columnar
CREATE Table Employee
(
Emp_Id Integer
,Dept_Id Integer
,First_Name Varchar(20)
,Last_Name Char(20)
,Salary Decimal (10,2)
)
No Primary Index
PARTITION BY COLUMN
(Emp_Id No Auto Compress
,Dept_id
(,First_name, Last_name, Salary)
No Auto Compress);
Columnar Partitions
Crete Table Order_table_PPI_Col
(Order_no integer not null
,Customer_no integer
,Order_date date
,Order_total decimal(10,2)
)
NO PRIMARY INDEX
PARTITION BY(Column
,Range_N(Order_date between date '2015-01-01 AND date '2015-12-31'
EACH INTERVAL '1' Month));
Columnar Table Fundamentals
- Columnar Tables must be a NoPI Table so No Primary Index (NoPI).
- The NoPI brings even distribution to the table.
- Columnar Tables allow Columns to be Partitioned.
- An AMP still holds the entire row, but partitions vertically.
- Columns are placed inside their own individual Container.
- All Containers have the same amount of rows in the exact order.
- Single Columns or Multi-Columns can be placed inside containers.
- Each container looks like a small table for I/O purposes.
- Add up all the containers and you rebuild the row.
- Columnar Tables make sense when users query only certain columns.
- When a row is deleted it is NOT Physically Deleted but marked deleted
Normal table vs columnar table
The two tables above contain the same Employee data, but one is a columnar table. Employee_Normal has placed 3 rows on each AMP with 5 columns. The other table Employee_Columnar has 5 Containers each with one column.
 |
| Add caption |
Example
CREATE Table Employee
(
Emp_Id Integer
,Dept_Id Integer
,First_Name Varchar(20)
,Last_Name Char(20)
,Salary Decimal (10,2)
)
No Primary Index
PARTITION BY COLUMN;
Columnar table
- This AMP is assigned 3 Employee Rows
- All AMPs hold 3 different Employee Rows also
- Each Row has 5 Columns
- This Columnar Table partitions in 5 separate containers
- Each container has a relative row number (1, 2, 3)
- Each container has the exact same number of rows
NoPI Table Capabilities:
- Are always Multi-Set Tables
- Have Secondary Indexes (USI or NUSI)
- Have Join Indexes
- Be Volatile or Global Temporary Tables
- Can COLLECT STATISTICS
- Be FALLBACK Protected
- Have Triggers
- Be Large Objects (LOBs)
- Have Primary Key Foreign Key Constraint
NoPI Table Restrictions
- No Primary Indexes allowed
- No SET Tables
- No Partition Primary Index (PPI) tables
- No Queue Tables
- No Hash Indexes
- No Identity Columns
- No Permanent Journaling
- Can't be the Target Table for any UPDATE, UPSERT or MERGE-INTO Statements
Examples of Columnar tables
Multi-Columnar
CREATE Table Employee
(
Emp_Id Integer
,Dept_Id Integer
,First_Name Varchar(20)
,Last_Name Char(20)
,Salary Decimal (10,2)
)
No Primary Index
PARTITION BY COLUMN
(Emp_Id
,Dept_id
(,First_name, Last_name, Salary));
Row Hybrid Columnar
CREATE Table Employee
(
Emp_Id Integer
,Dept_Id Integer
,First_Name Varchar(20)
,Last_Name Char(20)
,Salary Decimal (10,2)
)
No Primary Index
PARTITION BY COLUMN
(Emp_Id No Auto Compress
,Dept_id
(,First_name, Last_name, Salary)
No Auto Compress);
Columnar Partitions
Crete Table Order_table_PPI_Col
(Order_no integer not null
,Customer_no integer
,Order_date date
,Order_total decimal(10,2)
)
NO PRIMARY INDEX
PARTITION BY(Column
,Range_N(Order_date between date '2015-01-01 AND date '2015-12-31'
EACH INTERVAL '1' Month));