In this Teradata 14 has released many domain specific function added NUMERIC data type, String functions and many of the functions supports regular expressions. These new functions are designed to be compatible to Oracle.
Here we are going to discuss about the following domain specific regular expression functions.
Now will discuss in detail of each function below
REGEXP_SUBSTR
This function extracts a substring from a source string that matches a regular expression pattern.
General Syntax:
REGEXP_SUBSTR (source_string, regexp_string, position_arg);
position_arg = (occurance_org, match_arg)
REGEXP_SUBSTR Function Example:
SELECT REGEXP_SUBSTR ('God Bless Mummy God Bless Daddy', 'bless', 1, 2, 'i')
In the above example
source_string = God Bless Mummy God Bless Daddy
regexp_string = Bless
position_arg = Find the second occurrence of the string that matches regular expression. 'i' indicates case insensitive.

REGEXP_REPLACE
This function replaces portions of the source string parameter that match a regular expression pattern with a replace string.
General Syntax:
REGEXP_SUBSTR (source_string, regexp_string, replace_string);
replace_string=(position_arg,occurance_org, match_arg)
REGEXP_REPLACE Function Examples:
SELECT REGEXP_REPLACE ('Hello World World', 'world', 'My', 1, 1,'i');
In this we are replacing the 1st occurrence of 'World' with 'My' by ignoring case specific.
SELECT REGEXP_REPLACE ('Godís Love is so wonderful.', 'God's', 'Mother', 1, 1, 'c');In this we are replacing the 1st occurrence of 'God's' with 'Mother' by considering with case specific with 'c'.
SELECT REGEXP_REPLACE('I love the buzz-buzz buzzing of the bee', 'buzz', 'BUZZ', 1, 2, 'c');
In this we are replacing the 2nd occurrence of 'buzz' with 'BUZZ' by considering the case specific with 'c'.

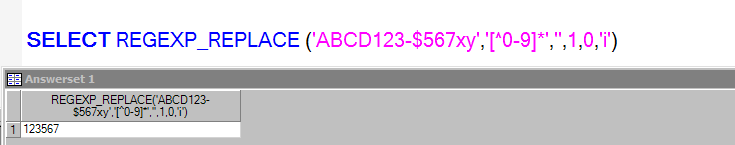
SELECT REGEXP_REPLACE ('ABCD123-$567xy','[^0-9]*','',1,0,'i');
In this we are replacing the any character or symbols with NULL. So it results only Numeric values.
REGEXP_INSTR
This function Search the source string for a match to a regular expression pattern and return the beginning or ending position of that match.
General Syntax:
REGEXP_SUBSTR (source_string, regexp_string, position_arg)
position_argt = (occurance_org,return_opt, match_arg)
return_opt returns 0 = function returns the beginning position of the match (default).
1 = function returns the end position
REGEXP_INSTR Function Examples:
SELECT REGEXP_INSTR('Happy Birthday to you', 'Happy Birthday', 1, 1, 0, 'c');
It returns 1
SELECT REGEXP_INSTR('Happy Birthday to you', 'Happy Birthday', 1, 1, 1, 'c');
It returns 15
REGEXP_SIMILAR
This function compares a source string to a regular expression and returns an integer value.
1 (true) if the entire string matches regexp_arg
0 (false) if the entire string does not match regexp_arg
General Snytax:
REGEXP_SIMILAR(source_string, regexp_string, match_arg)
REGEXP_INSTR Function Examples:
SELECT Emp_Name
FROM Emp_Table
WHERE REGEXP_SIMILAR (emp_name, '(Smith B(i|y)rd)|| (John B(i|y)rd)','c') = 1;
It returns the names of employees that match
Smith Byrd
Smith Bird
John Bird
John Byrd
REGEXP_SPLIT_TO_TABLE
This table function splits a source string into a table of strings using a regular expression as the delimiter.
General Snytax:
REGEXP_SPLIT_TO_TABLE (source_string, regexp_string, match_arg)
REGEXP_SPLIT_TO_TABLE Function Examples:
CREATE TABLE split_table_latin(id integer, src varchar(100) character set latin, pattern varchar(100) character set latin, match varchar(100) character set latin);
INSERT into split_table_latin(3, 'The2134quick234brown234fox987jumps8743over342the03487lazy089734red972384dog2343.', '[0-9]*','c');
Then the following SELECT statement:
SELECT * from table ( regexp_split_to_table(split_table_latin.src,split_table_latin.pattern,split_table_latin.match)returns (res varchar(100) character set latin)) as t1;
Returns a table with the following rows
Here we are going to discuss about the following domain specific regular expression functions.
- REGEXP_SUBSTR
- REGEXP_REPLACE
- REGEXP_INSTR
- REGEXP_SIMILAR
- REGEXP_SPLIT_TO_TABLE
Now will discuss in detail of each function below
REGEXP_SUBSTR
This function extracts a substring from a source string that matches a regular expression pattern.
General Syntax:
REGEXP_SUBSTR (source_string, regexp_string, position_arg);
position_arg = (occurance_org, match_arg)
REGEXP_SUBSTR Function Example:
SELECT REGEXP_SUBSTR ('God Bless Mummy God Bless Daddy', 'bless', 1, 2, 'i')
In the above example
source_string = God Bless Mummy God Bless Daddy
regexp_string = Bless
position_arg = Find the second occurrence of the string that matches regular expression. 'i' indicates case insensitive.

REGEXP_REPLACE
This function replaces portions of the source string parameter that match a regular expression pattern with a replace string.
General Syntax:
REGEXP_SUBSTR (source_string, regexp_string, replace_string);
replace_string=(position_arg,occurance_org, match_arg)
REGEXP_REPLACE Function Examples:
In this we are replacing the 1st occurrence of 'World' with 'My' by ignoring case specific.
SELECT REGEXP_REPLACE ('Godís Love is so wonderful.', 'God's', 'Mother', 1, 1, 'c');
SELECT REGEXP_REPLACE('I love the buzz-buzz buzzing of the bee', 'buzz', 'BUZZ', 1, 2, 'c');
In this we are replacing the 2nd occurrence of 'buzz' with 'BUZZ' by considering the case specific with 'c'.

SELECT REGEXP_REPLACE ('ABCD123-$567xy','[^0-9]*','',1,0,'i');
In this we are replacing the any character or symbols with NULL. So it results only Numeric values.
REGEXP_INSTR
This function Search the source string for a match to a regular expression pattern and return the beginning or ending position of that match.
General Syntax:
REGEXP_SUBSTR (source_string, regexp_string, position_arg)
position_argt = (occurance_org,return_opt, match_arg)
return_opt returns 0 = function returns the beginning position of the match (default).
1 = function returns the end position
REGEXP_INSTR Function Examples:
SELECT REGEXP_INSTR('Happy Birthday to you', 'Happy Birthday', 1, 1, 0, 'c');
It returns 1
SELECT REGEXP_INSTR('Happy Birthday to you', 'Happy Birthday', 1, 1, 1, 'c');
It returns 15
REGEXP_SIMILAR
This function compares a source string to a regular expression and returns an integer value.
1 (true) if the entire string matches regexp_arg
0 (false) if the entire string does not match regexp_arg
General Snytax:
REGEXP_SIMILAR(source_string, regexp_string, match_arg)
REGEXP_INSTR Function Examples:
SELECT Emp_Name
FROM Emp_Table
WHERE REGEXP_SIMILAR (emp_name, '(Smith B(i|y)rd)|| (John B(i|y)rd)','c') = 1;
It returns the names of employees that match
Smith Byrd
Smith Bird
John Bird
John Byrd
REGEXP_SPLIT_TO_TABLE
This table function splits a source string into a table of strings using a regular expression as the delimiter.
General Snytax:
REGEXP_SPLIT_TO_TABLE (source_string, regexp_string, match_arg)
REGEXP_SPLIT_TO_TABLE Function Examples:
CREATE TABLE split_table_latin(id integer, src varchar(100) character set latin, pattern varchar(100) character set latin, match varchar(100) character set latin);
INSERT into split_table_latin(3, 'The2134quick234brown234fox987jumps8743over342the03487lazy089734red972384dog2343.', '[0-9]*','c');
Then the following SELECT statement:
SELECT * from table ( regexp_split_to_table(split_table_latin.src,split_table_latin.pattern,split_table_latin.match)returns (res varchar(100) character set latin)) as t1;
Returns a table with the following rows
- The
- quick
- brown
- fox
- jumps
- over
- the
- lazy
- red
- dog
- .
This all about the Regular Expression Functions. I hope you enjoyed while learning.